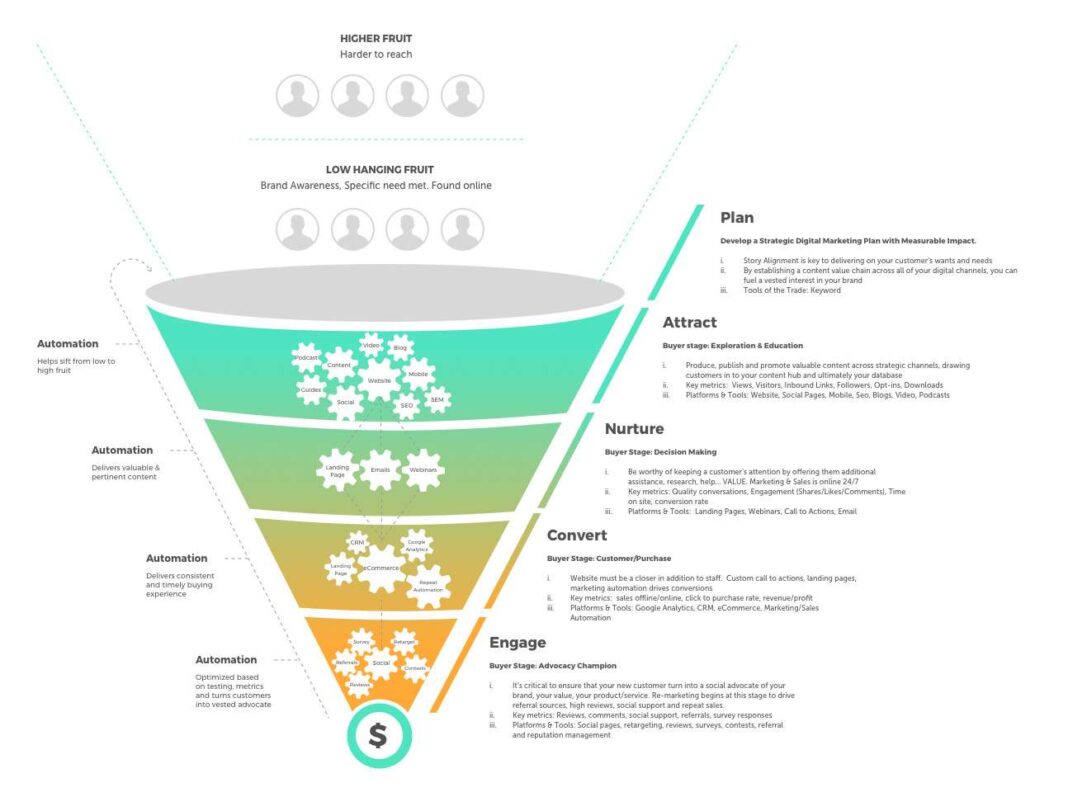
A digital marketing strategy for ecommerce is a structured plan that uses online channels, data, and technology to attract shoppers, convert visits into sales, and retain customers over time. In competitive markets like the US and UK, success depends less on isolated tactics and more on how channels work together across the entire customer journey.
This guide presents a clear, end-to-end framework you can apply to most ecommerce models—whether you sell physical products, digital goods, or subscriptions.
What a Digital Marketing Strategy for Ecommerce Really Means
An effective ecommerce strategy aligns audience insight, channel selection, content, paid media, data, and operations into one coherent system. The objective is not just traffic, but profitable growth and customer lifetime value.
Key outcomes include:
-
Predictable demand generation
-
Efficient acquisition costs
-
Higher conversion rates
-
Repeat purchases and retention
-
Measurable return on spend
Step 1: Define Clear Business and Marketing Objectives
Start with outcomes, not channels.
Common Ecommerce Objectives
-
Increase qualified traffic
-
Improve conversion rate
-
Grow average order value
-
Reduce acquisition costs
-
Increase repeat purchase rate
Translate business goals into measurable marketing targets (for example, improving conversion rate or reducing cost per acquisition).
Step 2: Understand the Ecommerce Customer Journey
A strong digital marketing strategy maps activity to each stage of the journey.
Awareness
Customers discover your brand.
-
Social content
-
Video
-
Influencer or creator exposure
-
Prospecting ads
Consideration
Customers compare options.
-
Product pages
-
Reviews and comparisons
-
Educational content
-
Retargeting
Conversion
Customers complete a purchase.
-
Optimised checkout
-
Clear pricing and delivery
-
Trust signals
-
Promotions or incentives
Retention
Customers return and advocate.
-
Email and lifecycle messaging
-
Loyalty programmes
-
Post-purchase content
-
Personalised offers
Aligning channels to each stage prevents wasted spend and improves efficiency.
Step 3: Choose the Right Channel Mix
No single channel drives ecommerce growth alone. Balance is essential.
Search Marketing
Captures high-intent demand.
-
Category and product visibility
-
Informational content that supports decisions
-
Competitive coverage for priority products
Social Media
Builds discovery and engagement.
-
Product launches
-
Community interaction
-
Creator partnerships
-
Short-form video
Paid Media
Accelerates scale and testing.
-
Search ads for intent
-
Social ads for discovery and retargeting
-
Display for remarketing
Email and Direct Messaging
Drives retention and lifetime value.
-
Welcome sequences
-
Abandoned cart reminders
-
Re-engagement campaigns
-
Post-purchase education
Each channel should have a defined role and success metric.
Step 4: Build Content That Sells Without Hard Selling
Content reduces friction in ecommerce decisions.
High-Impact Content Types
-
Buying guides and explainers
-
Product comparisons
-
Use-case demonstrations
-
Reviews and social proof
-
Short-form and long-form video
Content should answer real customer questions and reduce uncertainty, especially for higher-consideration purchases.
Step 5: Optimise Product Pages for Conversion
Product pages are the heart of ecommerce marketing.
Conversion Essentials
-
Clear value proposition
-
High-quality visuals
-
Concise, benefit-led copy
-
Reviews and ratings
-
Transparent pricing and delivery
-
Mobile-first design
Marketing traffic is wasted if product pages are not optimised to convert.
Step 6: Use Data to Guide Decisions
Data turns strategy into a repeatable system.
Core Metrics to Track
-
Traffic by channel
-
Conversion rate
-
Cost per acquisition
-
Average order value
-
Customer lifetime value
-
Retention and repeat rate
Analyse performance by channel and stage of the funnel, not just overall sales.
Step 7: Leverage Automation and Personalisation
Automation improves efficiency and relevance.
Common Automation Areas
-
Email flows based on behaviour
-
Product recommendations
-
Audience segmentation
-
Retargeting rules
Personalisation increases relevance without increasing workload.
Step 8: Align Technology With Marketing Strategy
Your ecommerce platform should support marketing execution and data access. Many businesses use platforms such as Shopify because they integrate analytics, advertising tools, and automation commonly used in the US and UK.
Platform choice affects:
-
Speed of experimentation
-
Data visibility
-
Marketing integrations
-
Scalability
Step 9: Manage Budget Allocation Intelligently
Budget decisions should reflect performance, not habit.
Practical Budget Principles
-
Invest more where margins are strong
-
Separate testing from scaling budgets
-
Adjust spend by funnel stage
-
Protect retention budgets during acquisition pushes
Regular reviews prevent overspending on underperforming channels.
Step 10: Build Trust and Compliance Into the Strategy
Trust is a conversion driver.
Trust Signals That Matter
-
Transparent policies
-
Secure checkout
-
Clear contact information
-
Honest product representation
-
Compliance with data and consumer regulations
In the US and UK, trust and compliance directly influence brand reputation and repeat purchases.
Step 11: Test, Learn, and Iterate Continuously
Ecommerce markets change quickly.
Ongoing Optimisation Areas
-
Creative messaging
-
Audience targeting
-
Offers and bundles
-
Page layouts
-
Checkout flow
Small, continuous improvements compound over time.
Common Mistakes in Ecommerce Digital Marketing Strategy
-
Chasing channels instead of outcomes
-
Over-investing in acquisition while neglecting retention
-
Ignoring data quality and attribution
-
Scaling before product-market fit
-
Treating channels as silos
Avoiding these mistakes improves profitability and resilience.
How Strategy Differs for Small vs Large Ecommerce Brands
Small Brands
-
Focus on niche positioning
-
Prioritise a few high-impact channels
-
Use content and community to compete on value
Larger Brands
-
Emphasise scale and efficiency
-
Coordinate omnichannel activity
-
Invest heavily in analytics and automation
The framework remains the same; execution depth changes.
Measuring Success Over Time
Success is not just monthly revenue.
Long-Term Indicators
-
Improving acquisition efficiency
-
Growing repeat purchase rate
-
Increasing lifetime value
-
Stable or improving margins
A strong digital marketing strategy compounds rather than spikes.
Final Thoughts on Digital Marketing Strategy for Ecommerce
A digital marketing strategy for ecommerce is a system, not a checklist. It connects customer insight, channels, content, data, and operations into a single growth engine.
For ecommerce businesses in the US and UK, sustainable success comes from:
-
Clear objectives
-
Journey-based planning
-
Balanced channel investment
-
Data-led decisions
-
Continuous optimisation
When executed with discipline and consistency, a well-designed strategy turns traffic into customers, customers into repeat buyers, and marketing into a predictable driver of long-term growth.